These are the main signs and symptoms of skin cancer, the risk factors, and when to see a dermatologist.
Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer worldwide, and early detection is crucial for effective treatment. Understanding the signs, symptoms, and risk factors associated with skin cancer can help you catch it early and increase the chances of successful treatment.
If you notice anything unusual, don’t hesitate to consult us at St. Louis Dermatology & Cosmetic Surgery.
Understanding Skin Cancer
- Types of Skin Cancer
- Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC): BCC is the most common form of skin cancer. It arises from the basal cells in the skin’s lowest layer. It typically appears in sun-exposed areas and grows slowly.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC): Originating from the squamous cells, SCC is more aggressive than BCC and can spread to other body parts if not treated.
- Melanoma: The most dangerous type of skin cancer, melanoma, develops in the melanocytes, the cells responsible for pigment. It can spread rapidly and become life-threatening if not caught early.
Risk Factors for Skin Cancer
Understanding your risk factors can help you be more vigilant. Key risk factors include:
- Excessive Sun Exposure: UV radiation from the sun is the leading cause of skin cancer, especially for those with a history of sunburn.
- Tanning Beds: Artificial UV light from tanning beds significantly increases your risk of developing skin cancer.
- Fair Skin: Individuals with fair skin, light-colored eyes, and blonde or red hair are at a higher risk.
- Family History: A family history of skin cancer, particularly melanoma, increases your risk.
- Age: The risk of skin cancer increases with age, though melanoma is also common in younger people.
- Personal History: If you’ve had skin cancer before, you’re at an increased risk of developing it again.
- Weakened Immune System: People with weakened immune systems, such as organ transplant recipients, are at higher risk.
- Exposure to Chemicals: Prolonged exposure to certain chemicals, like arsenic, can increase risk.
Recognizing the Signs of Skin Cancer
The key to early detection is being aware of changes in your skin. Here’s what to look for:
- ABCDEs of Melanoma:
- Asymmetry: One half of the mole or spot doesn’t match the other.
- Border: The edges are irregular, ragged, or blurred.
- Color: The color is not uniform and may include shades of brown, black, pink, red, white, or blue.
- Diameter: Melanomas are usually larger than 6mm (about the size of a pencil eraser) but can be smaller when first detected.
- Evolving: The mole or spot changes in size, shape, or color over time.
- Non-Melanoma Skin Cancers:
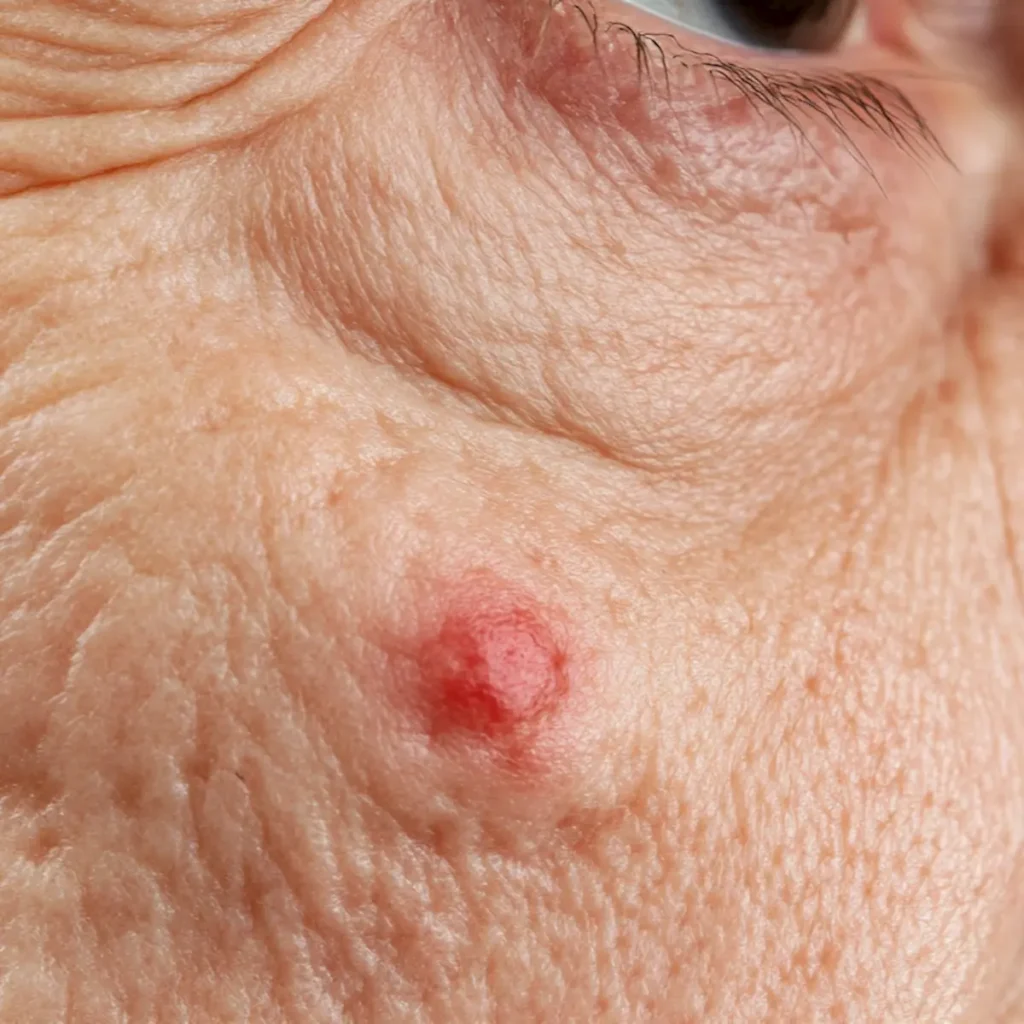
- Basal Cell Carcinoma: Often appears as a pearly or waxy bump, a flat, flesh-colored, or brown scar-like lesion, or a bleeding or scabbing sore that heals and returns.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: May present as a firm, red nodule, a flat lesion with a scaly, crusted surface, or a sore that heals and reopens.
- Unusual Symptoms:
- New Growths: Any new growths on your skin, especially those that grow quickly, should be examined by a dermatologist.
- Sores That Don’t Heal: Any sore that doesn’t heal within a few weeks should be checked.
- Itching or Tenderness: A spot that becomes itchy, tender, or painful warrants attention.
- Changes in Sensation: A mole or lesion that starts to itch, bleed, or feel tender needs to be evaluated.
Prevention and Protection
While you can’t eliminate the risk of skin cancer, there are steps you can take to reduce your chances:
- Use Sunscreen: Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 daily, even on cloudy days.
- Avoid Peak Sun Hours: Avoid the sun between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., when UV rays are strongest.
- Wear Protective Clothing: Cover your skin with long sleeves, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses.
- Avoid Tanning Beds: The UV light from tanning beds is harmful and increases your risk of skin cancer.
- Check Your Skin Regularly: Early detection is critical to successful treatment, so make self-exams a habit.
When to See a Dermatologist
If you notice any suspicious changes in your skin, you should see a dermatologist. Specifically, seek medical attention if you observe:
- If this is a new growth that looks different from other moles or spots.
- A sore that doesn’t heal or keeps coming back.
- Any of the ABCDEs of melanoma in a mole or spot.
- A change in an existing mole, such as an increase in size, change in color, or irregular borders.
Your dermatologist may perform a biopsy, in which a small skin sample is removed and examined under a microscope to determine whether cancer cells are present.
Contact Us Today
Knowing the signs of skin cancer is critical to catching it early. If you notice anything unusual, don’t hesitate to consult us at St. Louis Dermatology & Cosmetic Surgery. Early detection and treatment can significantly increase the chances of successful outcomes.
Remember, when it comes to skin cancer, it’s always better to be safe than sorry. Protect your skin, stay informed, and be proactive about your health.
GET IN TOUCH


This post is great. Compared to other posts I’ve seen recently, this one is exceptional. Thank you very much for this excellent post. I genuinely appreciate it!
Хотите привлечь больше покупателей и повысить доход?
Наше SEO-агентство продвинет ваш сайт на первые страницы Google и Яндекс.
Комплексное [url=https://olit.su/]SEO-продвижении[/url]: аудит, оптимизация, создание контента.
Прозрачная работа, опыт 10+ лет и реальные кейсы.
Начните получать трафик и заказы уже через 30 дней!